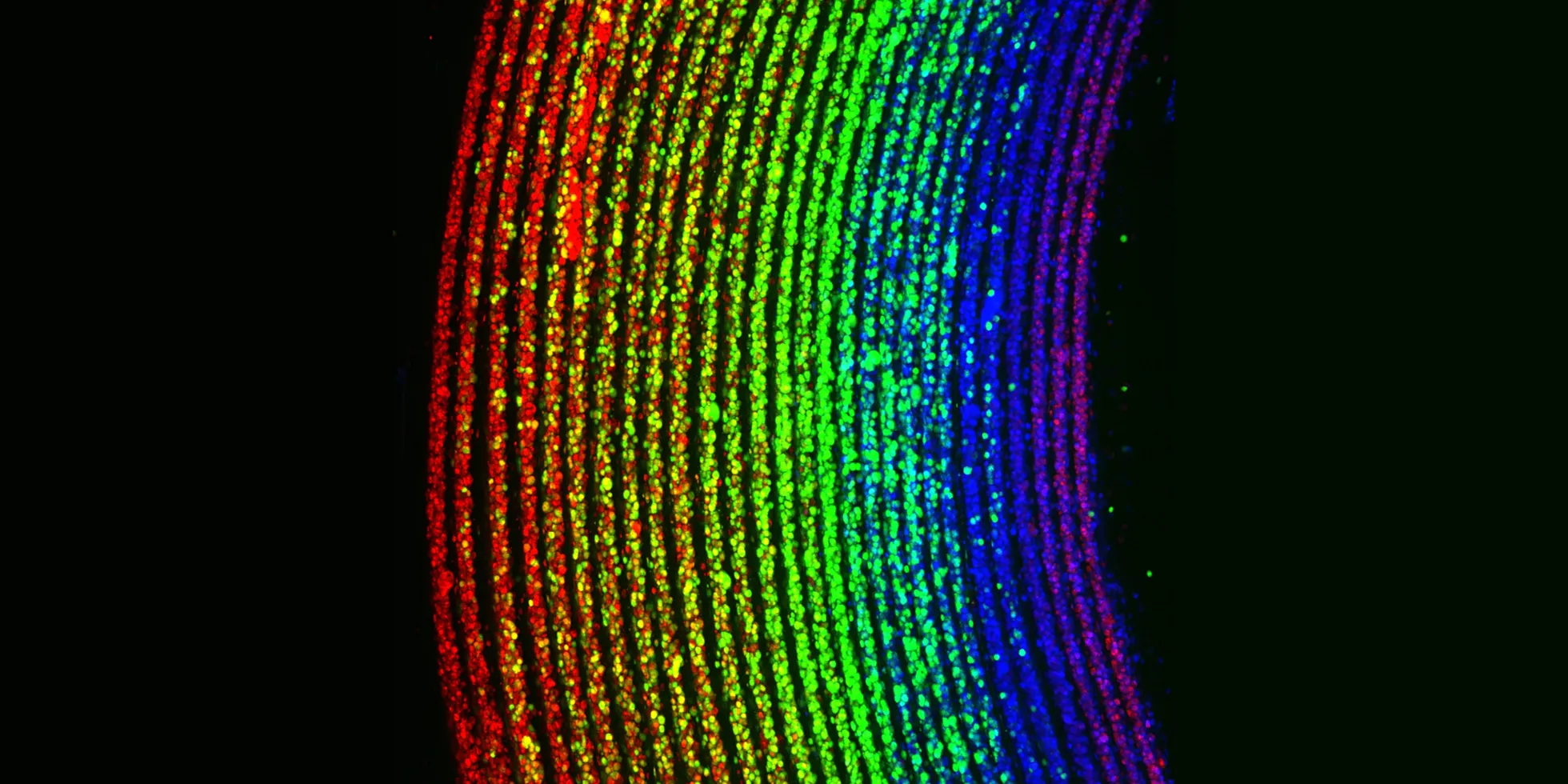
The technique, known as RIFLE – rotational internal flow layer engineering – enables the construction of separate layers as delicate as one cell thick.
Such versatility is crucial to developing accurate human models of layered tubular tissue for use in research, offering an important alternative to animal models, experts say.
Super-thin layers
Scientists have been able to demonstrate the technology by manufacturing cells into super-thin layers that mirror those seen in a human blood vessel.
Layered tubular tissue is found throughout the body – in blood vessels, the digestive tract and other organs. It can feature multiple cell types, generating layers with different properties and functions.
Current methods used to manufacture human tissue in the lab – known as biofabrication – can lack the detail needed to mimic these complex structures.
Rotating tube
Developed by experts at the University of Edinburgh, RIFLE is a low-cost and fast biofabrication method that can work to a very small scale.
The technique involves injecting a small volume of liquid containing cells into a tube rotating at high-speed – up to 9000rpm. The speed of the rotation causes the cells to distribute evenly across the internal surface of the tube, with higher speeds resulting in thinner layers.
When this process is repeated, it builds up cell layers to create a tubular structure made of different, distinct layers, with a high density of cells.
Lifelike tissue
The ability to economically create layered tubular tissue in the lab could offer an important model for drug development, experts say. Accurate human models of intestinal tissue could allow companies to monitor how medicines taken orally are absorbed in the gut.
With the RIFLE technology, we can create, in the laboratory, the high-resolutions that we observe in human layered tubular tissue, such as blood vessels.
Crucially, this uses the same materials and cells we find in our own bodies. This level of accuracy is essential for researchers who want to develop new medicines and investigate diseases – ultimately reducing the need for experiments involving animals.
Dr Ian Holland
Project lead, the University of Edinburgh
Working with the University’s commercialisation service, Edinburgh Innovations, the team has now patented the RIFLE technology and is working to develop further applications of this novel technique.
Developers of RIFLE caution that further testing and clinical studies are needed before lab-grown tissue is available for use in human transplants.
The technology was developed by scientists from the Universities of Edinburgh and Strathclyde and has been supported by EU Horizon 2020, EPSRC, BBSRC and WT iTPA funding.
Related links
Read the study in the journal Biofabrication
Image credit: Ian Holland

